Plants obtain their nutrition by various modes. The mode of nutrition can be divided into four distinct types. Broadly speaking, plants can be divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Heterotrophic plants can be further divided into parasites, saprophytes and symbiotic plants.
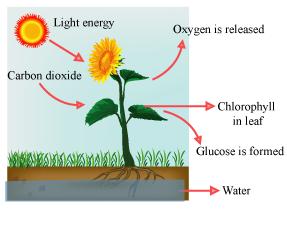
In plants, the green pigments called chlorophyll collect simple substances like water and salts from the soil and CO2 from the air, and using sunlight as a source of energy, convert the simple substances into complex food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis.
Leaves are the food factories of a plant. However, other parts of the plant play important roles, too. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
- Photosynthesis takes place in the leaves.
- The lower epidermis has openings called the stomata.
- The stomata take in carbon dioxide from the air.
- Chlorophyll captures energy from sunlight, and uses it to prepare food from carbon dioxide and water.
All chlorophyll-containing plants, including algae, and some plants with red, brown or other dominant pigment, make food using this process. Thus, both sunlight and trees are essential to sustain life on Earth. As we saw, during photosynthesis, plants produce food in the form of glucose.
This is then converted into complex compounds called carbohydrates, like starch and cellulose. Plants also prepare proteins with the help of nitrogen, which is obtained from the soil. Thus, the minerals dissolved in water are used to convert sugar into carbohydrates, proteins and fats. These food components form the source of energy for other heterotrophic plants and animals.
The insectivorous mode of nutrition is observed in plants such as the pitcher plant and the Venus fly trap.
- Heterotrophic plants don’t have chlorophyll, and are, therefore, unable to produce food using the process of photosynthesis.
- They obtain food from other plants by following either a parasitic, saprophytic or some other form of symbiotic relation with them for food.
This mode of nutrition is called saprtorophic nutrition. Plants that use the saprotrophic mode of nutrition are called saprotrophs.
Plants get nitrogen from the soil by a mechanism of symbiosis.
- A bacterium called rhozobium plays an important role in symbiotic nitrogen fixation.
- This type of nitrogen fixation is observed in plants like peas, moong beans and other legumes.
- By this process, both bacteria and plants get benefited mutually.
We get nutrients from vegetables, fruits or meat.
We directly or indirectly depend on plants for our nourishment.
Plants that make their own food are called autotrophs.
Plants that depend on others plants for nourishment are called heterotrophs.
Chlorophyll is the green pigment present in plants. Plants collect simple substances like water and salts from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air. Then, using sunlight as a source of energy, plants convert simple substances into complex food. This process is called photosynthesis.
The word photosynthesis is derived from two words – photo, meaning ‘light’, and synthesis, meaning ‘to combine’.
Leaves are the food factories of a plant. The roots help by absorbing water and minerals from the soil. The stem or trunk helps by conducting water and minerals to the leaves. The actual process of photosynthesis takes place in the leaves.
The epidermis of the leaf is protected by a thin layer of cuticle.
The lower epidermis has openings called stomata, which aresurrounded by guard cells. The stomata take in carbon dioxide from the air.
The area above the lower epidermis is called the vein, which contains vessels to bring water and minerals to the leaf. Above this is a layer containing palisade cells that have green pigments, called chlorophyll, which capture energy from sunlight and use it to prepare food from carbon dioxide and water.
The by-products are oxygen and water, which are released through the stomata during daytime. The food is sent to other parts of the plant through the veins.
During photosynthesis, plants produce food in the form of glucose, which is furtherconverted into complex compounds like starch and cellulose.
Plants also prepare proteins with the help of nitrogen, which is obtained from the soil. Micro-organisms convert atmospheric nitrogen into water-soluble compounds, which are absorbed by the roots of plants.
The insectivorous mode of nutrition is seen in plants such as the pitcher plant and the Venus fly trap. Due to a lack of nutrients like nitrogen and other minerals in the soil, their leaves are modified to form a trap with hairy walls that can capture insects.
Once an insect enters the trap, the lid of the trap closes, and the prey gets entangled in the hair. The plant then digests its prey to obtain the required nutrients.
Heterotrophic plants do not have chlorophyll, and cannot produce food by photosynthesis.
The cuscuta plant derives valuable nutrients from the host plant, so it is called parasitic.
Fungi obtain their nutrition from dead and decaying organic matter. They secrete digestive juices onto dead and decaying matter, and then absorb the nutrients from it.
Plants that use saprotrophic nutrition are called saprotrophs. The mode of nutrition in which organisms take in nutrients in solution form from dead and decaying matter is called saprotrophic nutrition.
Fungi reproduce using spores that germinate and grow into a new fungus.
Rhizobium bacteria form a symbiotic relationship with plants such as gram, peas, moong beans and other legumes.